Building and Running the Docker Containers
Objective
This lab walks you through the process of building container images for our python-fastapi-demo-docker project and running them as distinct services using Docker Compose or equivalent Finch commands. By the end, you'll know how to manage your multi-service applications more effectively, ensuring smoother development, deployment, and updates.
Prerequisites
Initial Setup
Navigate to the root directory of the python-fastapi-demo-docker project where your environment variables are sourced:
cd ~/environment/python-fastapi-demo-docker
1. Building Docker Images for Each Service
Build Docker images for the application and database services by running:
docker-compose build
Alternatively, if you're using Finch, run the following command to build the container images for the application and database:
finch compose build
This builds Docker images based on the configurations in the docker-compose.yml file. Docker follows the Dockerfile instructions during each service's build process, creating separate images for the 'python-fastapi-demo-docker-web' and 'python-fastapi-demo-docker-db' services.
2. Running the Services as Docker Containers
After building the images, start the application and database services in separate Docker containers using:
docker-compose up
Alternatively, if you're using Finch, run the following command to start the application and database services:
finch compose up
This command initiates containers for each service as specified in the docker-compose.yml file. Don't stop the command execution to keep application and database services running.
Use the tabs below to see the steps for the specific environment where you are running this lab.
- AWS Workshop Studio
- Local Computer
Execute the command below in a new VScode terminal to show the URL to connect to FastAPI application:
echo "http://$PUBLIC_IP:8000"
Access this URL using your web browser.
Upon navigating to http://localhost:8000 in your browser, you should see the FastAPI application running.
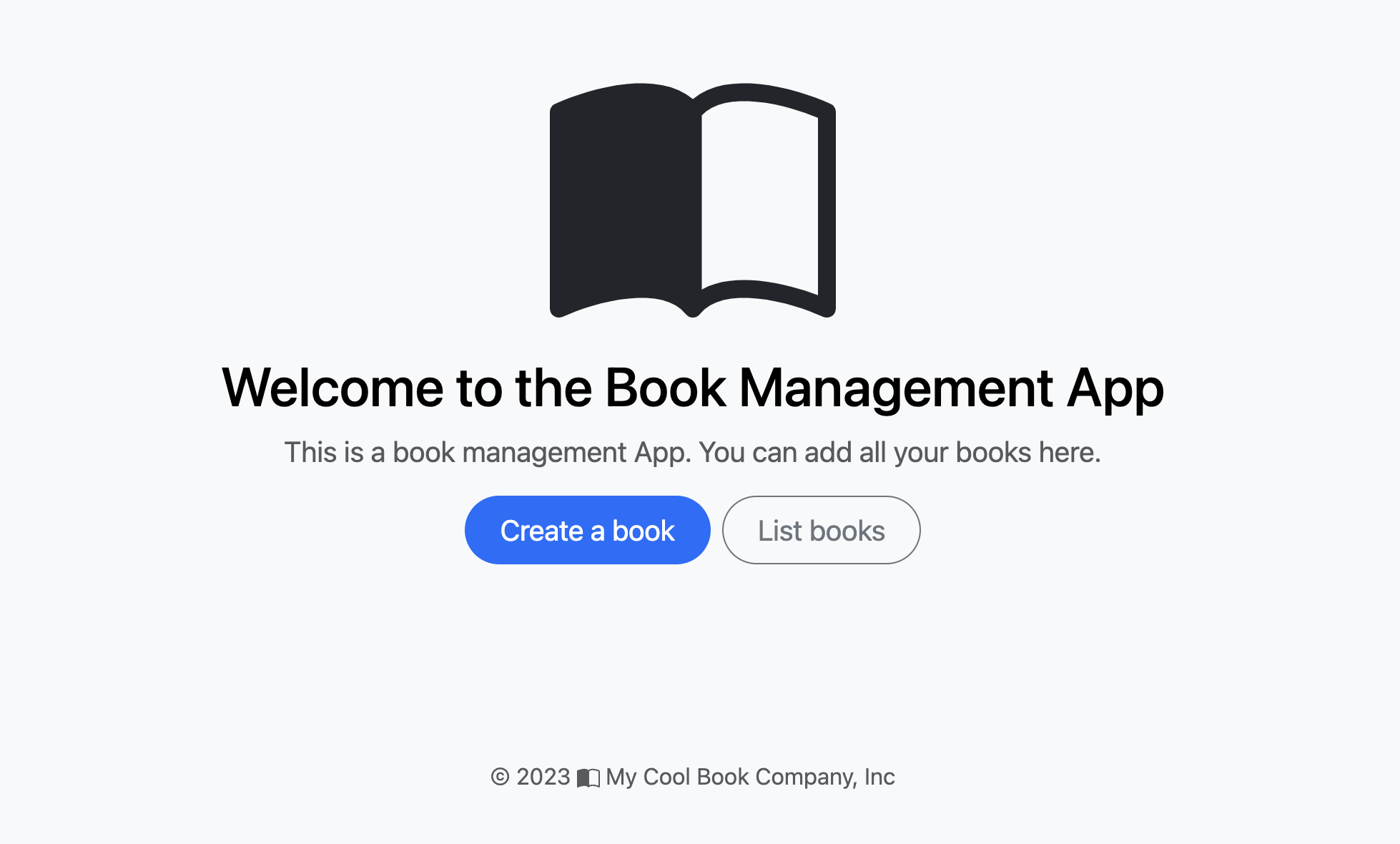
3. Verify the Setup by Adding a Book
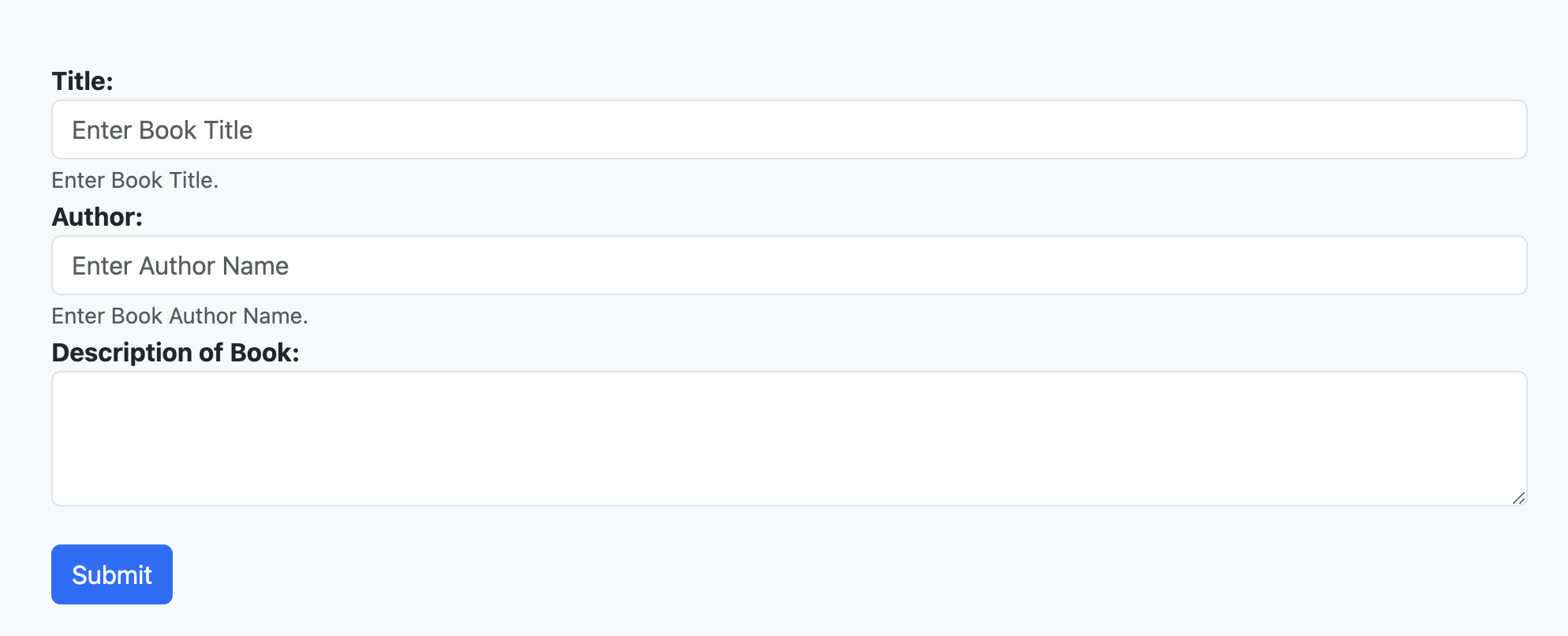
To confirm that everything is functioning as expected, attempt to add a book by selecting the Create a book option.
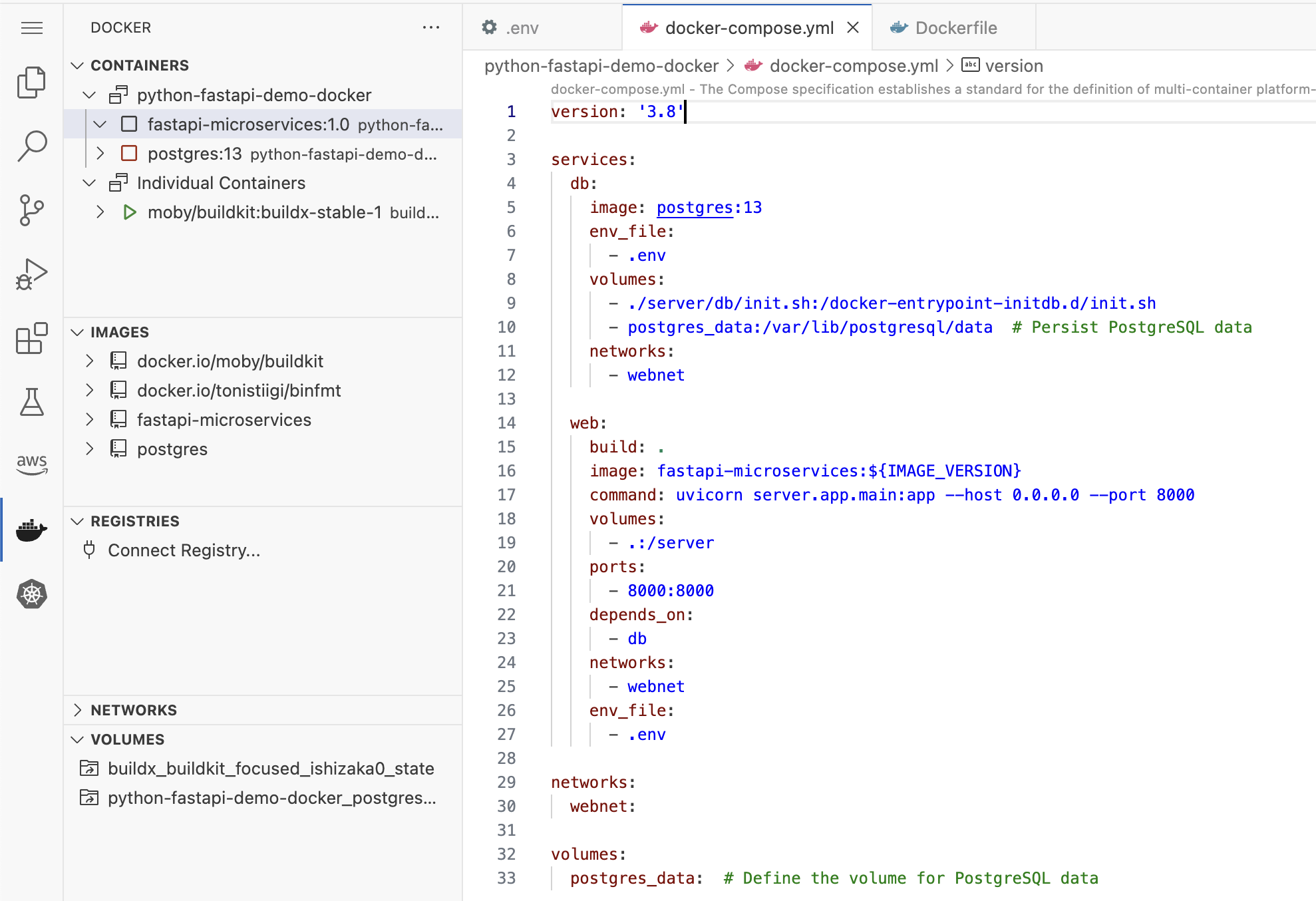
4. Interpreting Containers
Your application ('python-fastapi-demo-docker-web' service) and your database ('python-fastapi-demo-docker-db' service) will operate in separate containers. The "Containers" tab in the Docker VS Code Extension shows the containers for our python-fastapi-demo-docker application, as instances of the services in our Docker Compose configuration.
5. Stopping the Services and Their Containers
Stop and remove the containers of both services by pressing CTRL + C and running the following command:
docker-compose down --volumes
Alternatively, if you're using Finch, press CTRL + C or run the following command to stop and remove the containers:
finch compose down
This command halts the containers and, by default, also removes the containers, networks, and volumes as described in your docker-compose.yml file.
6. Rebuilding and Restarting Docker Services
To rebuild the images and restart the services simultaneously, execute the following command:
docker-compose up --build
Alternatively, if you're using Finch, run the following command:
finch compose up --build
This rebuilds the Docker images, and starts the services with the new images, ensuring your services are always operating with the latest application version.
7. Stopping the Services and Removing Their Containers
Then again, stop and remove the containers of both services by pressing CTRL + C and running the following command:
docker-compose down --volumes
Alternatively, if you're using Finch, press CTRL + C and run the following command to stop and remove the containers:
finch compose down
This command halts the containers and also removes the containers, networks, and volumes as described in your docker-compose.yml file.
Conclusion
This lab explored the process of constructing and executing Docker containers using Docker Compose in the 'python-fastapi-demo-docker' project. This approach provides an efficient way to manage multi-service applications, which greatly benefits developers by streamlining the process.