Containers
Overview
This chapter introduces the process of containerizing an application, emphasizing the creation of multi-architecture images compatible with Kubernetes. Subsequently, we'll show how to deploy these images to a private Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) and manage them within a Kubernetes environment.
Objective
This guide aims to introduce essential concepts and practices related to containerization. It focuses on familiarizing you with the benefits of containerization, the role of Amazon ECR as a container registry, the importance of multi-architecture images for Kubernetes, and how Kubernetes uses containerization for efficient application deployment and management.
Terms
Containerization is a method of running applications in isolated environments, each with its own resources. In the context of Kubernetes, container images should be multi-architecture to ensure compatibility across different node architectures.
-
A container image is a self-contained, lightweight package holding everything necessary to run an application. It comprises a series of read-only layers, each layer signifying a modification to its predecessor. For compatibility with Kubernetes, it's crucial to make container images multi-architecture. These images are stored in a container registry and can be deployed on any system supporting containerization.
-
A container is a running instance of a container image, operating as a process on a host system. With its unique file system, network interface, and resource set, it's isolated from other containers and the host system. Containers are transient, capable of swift creation, commencement, halting, and deletion.
-
A container registry is a centralized platform for storing, managing, and distributing container images. It acts as a repository, facilitating easy image access and retrieval across various hosts or environments. Container registries can be public or private, reflecting the organization's security needs. While public registries like Docker Hub allow unrestricted image upload and access, private ones like Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) cater to enterprise applications.
-
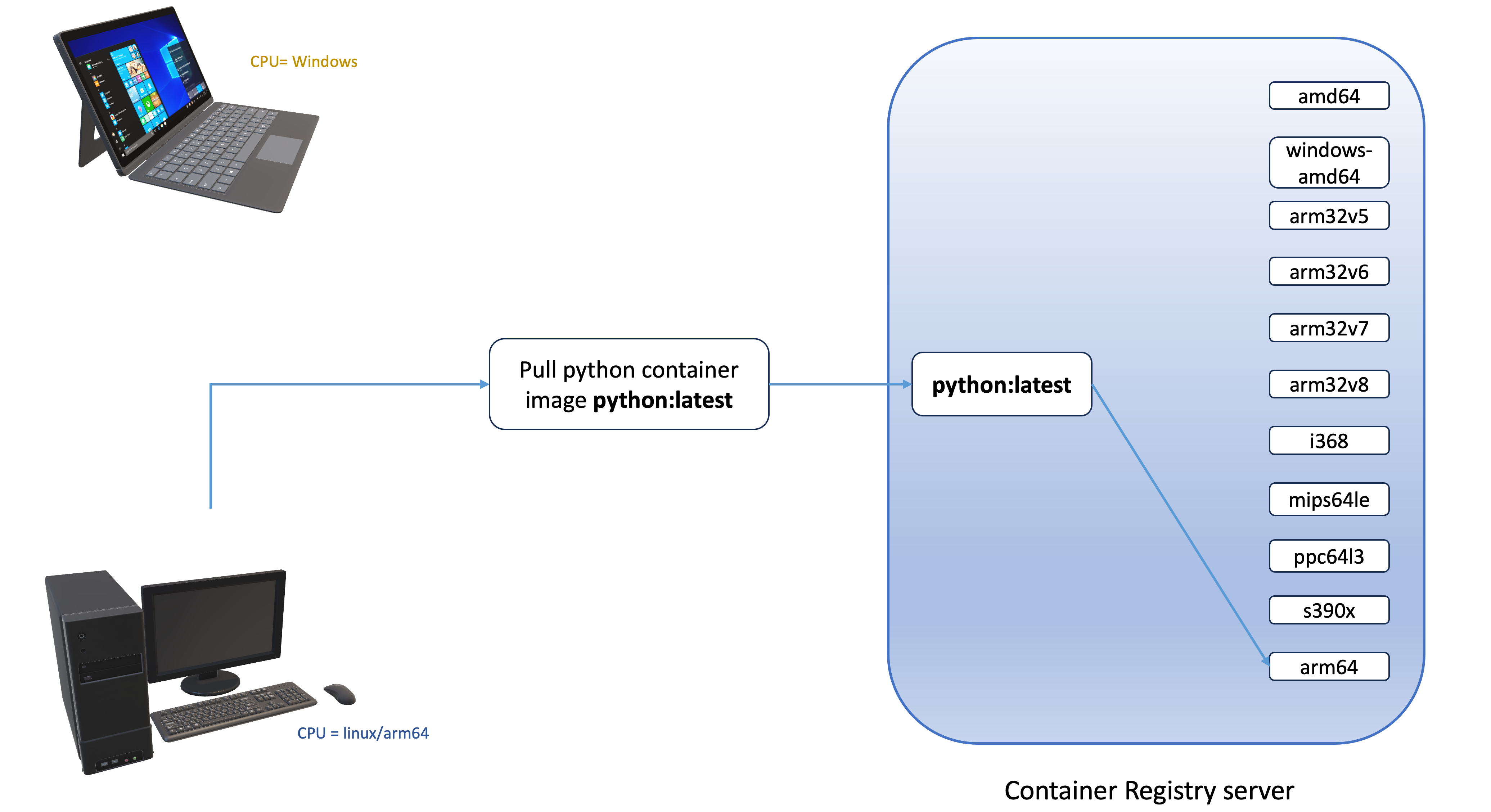
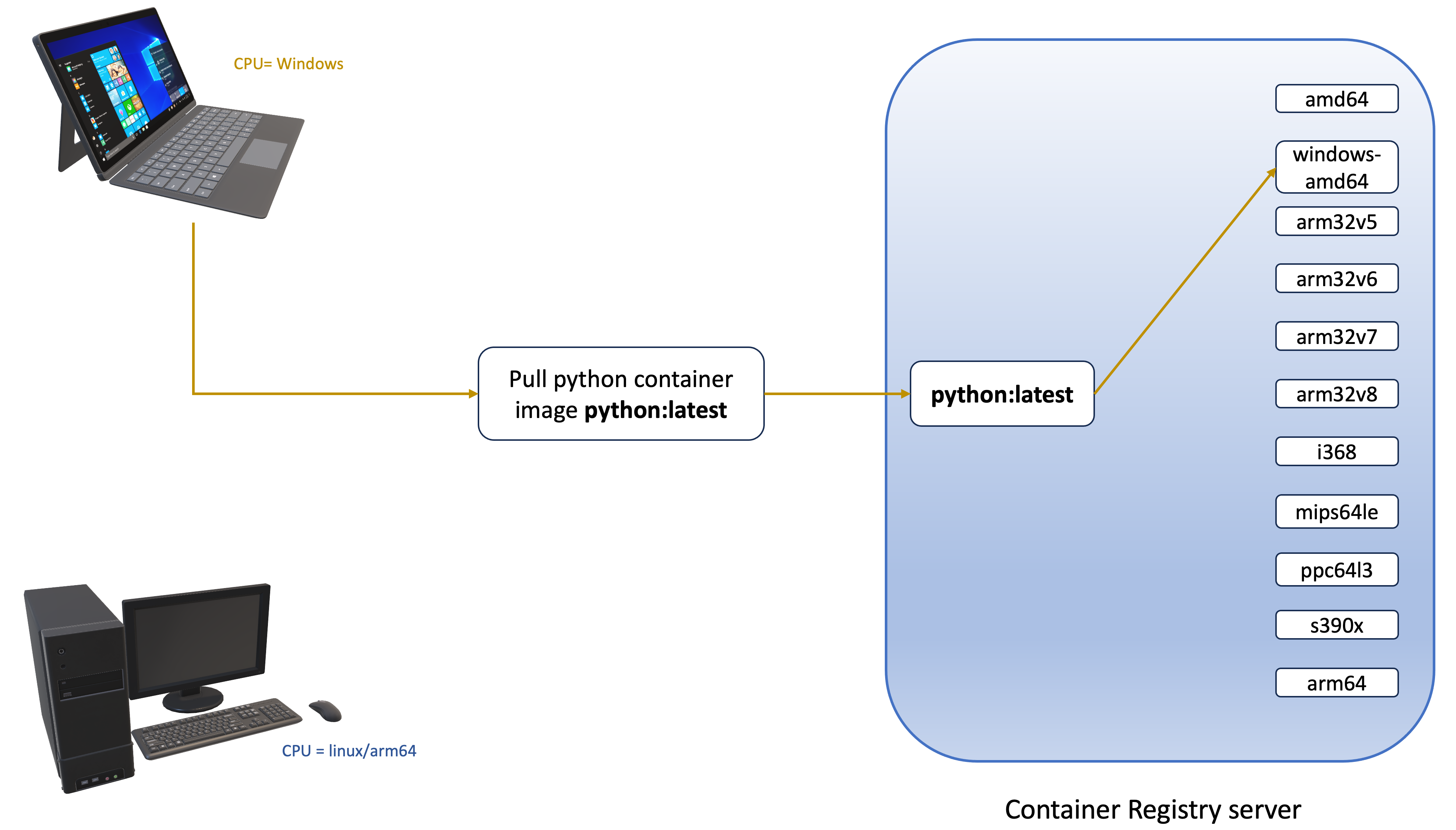
In the context of containers, multi-architecture refers to the ability of a container image to run on multiple CPU architectures (e.g.,
linux/amd64,linux/arm64,windows/amd64). A multi-architecture container image is nothing but a list of images that have references to binaries and libraries compiled for multiple CPU architectures. An important advantage of multi-architecture containers is the ability to deploy highly available applications in a Kubernetes cluster that can be made up of nodes with different CPU architectures (x86-64, ARM64, Windows). Let's explore multi-architecture images across various container registries, such as an ECR public repository and DockerHub. In the following example, the docker/library/python image on ECR supports multiple architectures like Linux, Windows, ARM64, and x86. The python image on DockerHub offers similar versatility.
- Linux/arm64
- Windows